
The thermostat is a very important part of internal combustion engines as it ensures that the ideal operating temperature is reached as quickly as possible and then maintained. For this purpose, this part feeds the coolant to one of the two coolant circuits by opening and closing. This component is designed for the service life of a vehicle and usually does not need to be serviced. However, contaminated cooling water or age-related wear can cause damage to the thermostat, which must be repaired as quickly as possible to ensure trouble-free operation of the engine. In this article you can find out what other causes a defect can have, how it becomes noticeable and how a defective thermostat is replaced.
Contents
What is a thermostat and how does it work he?
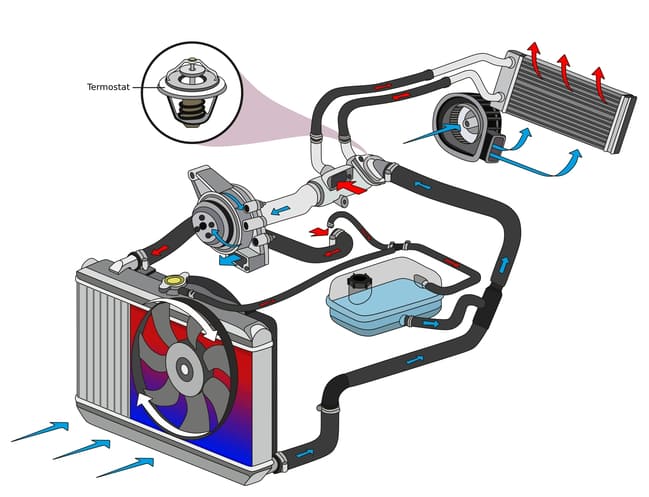
The main function of a car's thermostat is to regulate the cooling water temperature, on the one hand to heat the engine to an optimal operating temperature as quickly as possible and on the other hand to protect it from overheating. To ensure this, this component works with two cooling water circuits, one small and one large. This component is designed as a valve that can open or close depending on the temperature of the coolant. When you start your car, the engine is usually still cold, which is why the thermostatic valve is closed. As a result, the coolant initially only circulates within the small cooling circuit, which includes the water pump, the heat exchanger for heating the vehicle interior and the engine block itself. As soon as the engine has reached its ideal operating temperature, usually between 80°C and 110°C, the thermostat opens and thus releases the large cooling water circuit so that the coolant can now flow to the cooling water cooler. There it is cooled by the headwind and then returned to the small cooling water circuit, cooling the engine in this way. If the engine gets too hot despite a large cooling water circuit, the car can switch on one or more cooling fans, which are particularly important at high speeds or high outside temperatures. This makes it possible to keep the engine temperature constant at the optimum and thus to ensure optimum combustion of the air-fuel mixture. This leads to reduced fuel consumption and lower pollutant emissions.
There are two different types of automotive thermostats available. On the one hand there is the conventional, mechanical thermostat and on the other hand the electrical, characteristic map thermostat. The two types basically work identically, as both open and close the inlet to the large cooling water circuit with the help of a spring plate. For this purpose, the mechanical thermostat uses an expanding material, usually wax, which expands or contracts depending on the temperature of the cooling water and thus opens or closes the path to the large cooling water circuit. With a map-controlled thermostat, on the other hand, this is controlled via an electric actuator, which is controlled by the engine control unit, which means that the cooling water temperature can be controlled more efficiently and quickly. The inlet to the large cooling water circuit is opened or closed each time the cooling water temperature reaches or falls below the opening temperature of the thermostat.
What happens if your car's thermostat is defective and what can cause a defect?
The thermostat is not an ordinary wearing part, but it can be damaged by mechanical influences.
The following causes are most commonly responsible for a defect in this component:
- ! blocked spring plate due to foreign bodies in the cooling water or corrosion
- !Thermostat hanging loosely in the cooling water flow due to broken holder on the thermostat housing
- ! Escaping expanding material/wax due to a leaking or damaged seal
- < span class="as-triangle" style="border-color: #333333">! Defective electric actuator due to ingress of cooling water
All these causes result in the thermostat either no longer being able to open or no longer being able to close. If it can no longer close, the large cooling water circuit remains switched on permanently, which means that the engine needs a longer time to reach its optimal operating temperature or does not reach it at all when the outside temperatures are cold. This leads to faster wear of all engine components and increased fuel consumption. If the thermostat no longer opens, i.e. is blocked when closed, the large cooling circuit can no longer be switched on to cool the coolant. This leads to overheating and overpressure in the cooling system, which in turn can damage connected parts such as the cylinder head, the cylinder head gasket, the engine mechanics, the cooling system or the radiator hose. In the worst case, damage to the moving components can even lead to engine damage. For this reason, it is particularly important to prevent possible damage to this component as early as possible, for example by flushing the car radiator. However, if your car's thermostat does break, it must be replaced as soon as possible to prevent worse consequential damage.
What are the symptoms that indicate a defective thermostat on your car ?

The symptoms of a defect differ depending on whether the part can no longer open or no longer close. A permanently open thermostat is usually noticeable when the engine does not reach its operating temperature at all or only after a long drive and/or the heating in the vehicle interior does not warm up. On the other hand, if the thermostat is permanently closed, the engine will quickly overheat, which is indicated by the coolant light coming on if your car has one.

Otherwise, this can also be easily recognized by the fact that the temperature gauge on the dashboard rises to more than 90°C. A leak can be detected when checking the cooling water tank, as the cooling water changes color and the leaked wax is clearly visible floating on the surface. Corroded or broken contacts of a characteristic map thermostat are immediately noted by the control unit as a fault in the error memory. A defect can also make itself felt through increased fuel consumption.
Can a defective thermostat be repaired or does it have to be replaced?
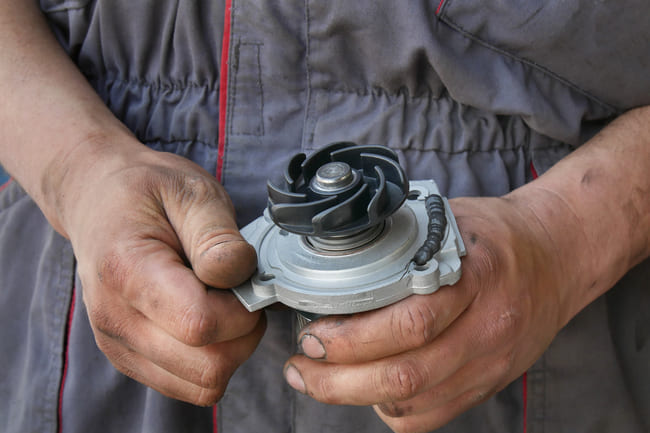

Whether you can still drive your car without a thermostat or whether you should switch it off immediately depends on whether it no longer opens or no longer closes. If the part is permanently open, you can continue driving, but you should completely avoid driving under full load due to the higher risk of wear. On the other hand, you should not continue driving with a permanently closed thermostat due to the risk of the engine overheating. In any case, you should visit a specialist workshop as soon as possible to have this component checked. If a defective thermostat is confirmed during inspection, it must be replaced with a new original or identical part.
The procedure depends on the vehicle model:
- Raise the car using a lifting platform
- Remove underride protection
- Drain cooling water
- Remove surrounding components, lines and water hoses to gain access to the thermostat housing
- Remove old thermostat
- Install new part and new seals
- Refill cooling water
- Bleed the coolant circuit
Depending on the installation position of the thermostat, a specialist needs a total of one to three hours for the exchange, which results in labor costs of around 100 to 300 euros. In addition, there are the material costs of around 20 to 50 euros for a mechanical thermostat or up to 250 euros for a characteristic map thermostat and the costs for new coolant of around 25 to 50 euros . So you have to reckon with costs of a total of 150 to 600 euros for changing this component.
Conclusion
Since the thermostat is an essential component the engine cooling system, unnoticed defects in this component can have particularly serious consequences. The part is particularly prone to failure as a result of contaminated coolant and age-related wear. The failure of a thermostat is particularly noticeable through overheating of the engine (thermostat valve no longer opens) or an extremely long warm-up phase of the engine (thermostat no longer closes). In this case, an inspection and replacement of the part is mandatory and should preferably be carried out by a specialist or a specialist workshop.
