
An internal combustion engine is made up of different components, with the cylinder head being one of the most complex parts. This is mounted on top of the engine block and connected to the crankcase via the cylinder head gasket. The cylinder head ensures the engine is cooled and lubricated by means of an intake and exhaust port. Because of this function, it is one of the most important components of internal combustion engines. If your car loses oil or the engine performance decreases, you should visit a specialist workshop as soon as possible to have it checked whether this is due to a defective cylinder head or a defective cylinder head gasket. In this article you can find out how you can identify a defect, how this part is structured and what its functions are.
Contents
Structure of the cylinder head
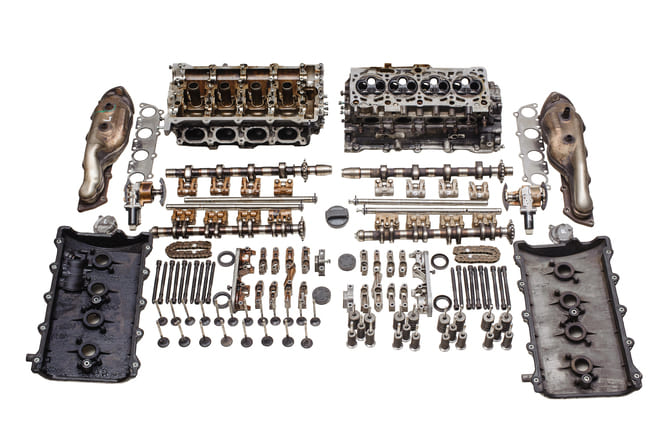
Because the cylinder head of a car is very complex, it is one of the most expensive parts of the engine. This part is usually made of light metal or aluminum alloys and is mounted directly on the crankcase below due to the extremely high forces it is subjected to. Special long screws, the so-called cylinder head screws, are used here, the preload of which has an elastically resilient effect on the bolts, which means that they can withstand higher loads and ensure the tightness of the engine. This component is closed at the top with a valve cover, also known as a cylinder head cover or cylinder head cover. The gap between the individual components is closed with the help of the cylinder head or valve cover gasket. The cylinder head consists of the following components, which differ slightly depending on whether the engine runs on petrol or diesel.
- Inlet and outlet valves: In diesel engines, air is drawn in here, in petrol engines an air-fuel mixture.
- Inlet and outlet ports: The intake air (diesel) or the air-fuel mixture (petrol) enters the cylinders and through them Exhaust gases can escape.
- Camshafts: They ensure that the valves open and close and are usually driven by driven by a timing chain, which in turn is driven by the crankshaft.
- Injectors/Injection nozzles: The valves are found in petrol engines and are used to inject fuel into the combustion chambers, while the nozzles in diesel engines are responsible for injecting fuel into the combustion or pre-chambers.
- Due to the high temperatures, the cylinder head must be cooled either with water or with air. Most modern vehicles use water cooling, which uses a mixture of water, antifreeze and anticorrosive as the coolant that flows from the crankcase through the head gasket and into the cylinder head. This enables significantly more effective cooling than air cooling, in which this component is only cooled with air that flows past the cylinder head through large cooling fins. The advantage of air cooling is cheaper and simpler construction, as well as more reliable operation, since the coolant does not freeze at low outside temperatures.
Functions of the cylinder head
One of the most important tasks of your car's cylinder head is to seal off the combustion chamber at the top and to constantly supply the engine block with air or an air-fuel mixture. To ensure an airtight connection between this part and the engine block, a cylinder head gasket is installed in between. With the help of the inlet and outlet channels, the cylinder head directs oil into the engine block in order to permanently lubricate the cylinders located there. In addition, the combustion heat can also be dissipated via water-carrying channels or cooling fins filled with air. Due to its function, this component is an indispensable part of the engine, as it ensures its smooth operation.
Causes and signs of defects

Unfortunately, the cylinder head is also prone to failure due to its complex structure and varied functions. The most common cause of a leaking cylinder head gasket is progressive wear. The material of the component itself can also tear, as it is exposed to extremely high temperatures, strong vibrations and overall high loads. Other causes of a defect in the cylinder head or its components are incorrect maintenance, material of inferior quality, missing or incorrect dosage of antifreeze and anti-corrosion agent in the coolant, insufficient lubrication and material wear due to advancing age or high mileage. Since a defective or leaking cylinder head can result in engine damage in the worst case, you should visit a specialist workshop for inspection immediately if you notice the following signs on your car:
- ! Engine power loss
- !Oil in the coolant
- ! Bad cold start behavior
- ! Water and oil need to be refilled within a short time
- ! Cooling water temperature too high
Cleaning of the cylinder head
When fuel is burned, carbon is a by-product that is also deposited on the cylinder head over time, forming a soot layer. This can harden more and more and ultimately limit the performance of this component. Therefore, not only the engine flushing is important for the perfect functioning of the engine, but also regular cleaning of the cylinder head.
To clean the part, the following steps must be performed:
- Remove all parts that block the way to the cylinder head
- Unscrew the cylinder head screws and remove the cylinder head
- Clean the component chemically or with blasting media
- Reinstall the cylinder head
- Reinstall all previously removed parts
When reinstalling, it is essential to ensure that each screw is screwed back in its original place, as these are often of different lengths. Also, be very careful and always wear safety goggles and solvent-resistant gloves to prevent skin and eye irritation. In addition, the cleaning agent must be precisely matched to the surface to be cleaned, as an incompatible agent can cause corrosion and serious damage.
Repair of the cylinder head
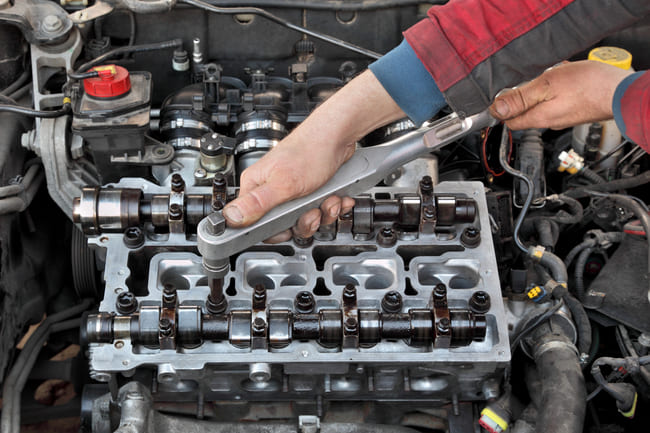

Unfortunately, most defects require complex and expensive repairs to the cylinder head. To do this, it usually has to be removed first and then ground flat after repairs to ensure the tightness between the cylinder head and engine block. It is very rarely necessary to change the complete cylinder head, as mostly replaceable parts, for example the valves, are damaged. If only the seal is leaking, you can also seal the part yourself. However, the sealants freely available for cylinder heads are not ideal and only serve as a temporary solution. However, if the cylinder head is broken, a repair is essential. Since this is extremely demanding and complex, it is strongly recommended that you have it overhauled in a competent specialist workshop. However, due to the high amount of work, a repair is often associated with very high costs in the range of several hundred to several thousand euros, depending on the vehicle model and engine. In order to save costs, a pressure test can first be used to test whether a cylinder head has cracked, since many cracks cannot be seen with the naked eye or are hidden. To do this, the component is first carefully cleaned, milled and welded. Then it is pressed and the cooling water channels are sealed. In the pressure tank, the cylinder head is subjected to a pressure of up to 30 bar as soon as it has reached its operating temperature of up to 80°C. Rising air bubbles are a clear sign of cracks in the material of this component. However, if the pressure test is passed, the cylinder head can continue to be used without any problems.
Conclusion
Due to its function, the cylinder head is unfortunately very susceptible to defects, which, however, are often noticeable through noticeable symptoms such as loss of performance, poor cold start behavior and oil loss. The repair of this component should only be carried out by a suitably trained specialist, as this is very complicated and labor-intensive due to the very complex structure of the part. After checking and subsequent repair, it is necessary to grind the cylinder head. This component also plays a crucial role in engine tuning, as this should not be carried out before the cylinder head has been processed so that it can cope with the increased performance. Cylinder head machining involves several steps from cleaning and disassembling the part, spinning on the seat rings, milling and smoothing the ports, through cutting the seat rings and machining the valves, to blasting, facing and assembling the cylinder head.
