
The common rail system is a fuel injection system used in used in modern diesel vehicles. Its main feature is the use of a common rail for all injectors, in which fuel is stored under high pressure (up to 300 MPa). The fuel is then fed to the pipe by a high pressure pump, then routed to the injectors and injected directly into the engine cylinders. The timing of the injection, the fuel metering and the number of injections per cycle are controlled by the engine control unit.
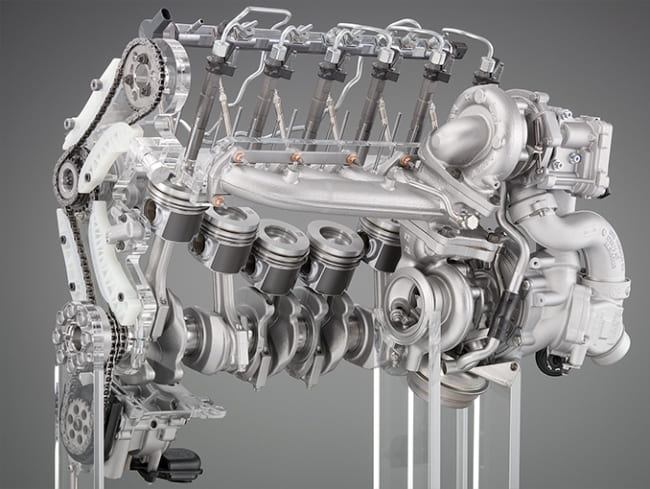
The common rail system has been installed in passenger cars since 1997. Diesel engines in most passenger and commercial vehicles are equipped with them today.
Contents
Engines with common-rail system
| Car Make | Engine Make | Engine Models |
| Nissan, Dacia, Renault | dCi | K9K, R9M, F9Q, R9N, M9R, G9T, G9U, M9T, P9X, V9X |
| Mercedes-Benz | CDI | OM646, OM611, OM651, OM647, OM612, OM648, OM668, OM628, OM629 |
| d | OM654, OM656 | |
| Opel, Vauxhall | CRI, CRI BiTurbo | X20DTL, Y20DTH, Z17DTL, Z17DTH , Z13DTH, Z19DTH |
| CDTi | Z17DTH, A17DT, A13DTE, A17DTJ, Z17DTJ, G9U 630, A17DTR, A20DTH, Z13DTJ, Z13DTH, Z19DTH | |
| BiTurbo CDTI | A20DTR, B20DTR | |
| Hyundai, KIA | CRDi | J3, D3FA, D4EB, D4CB, D4FC, D4FA, D4FB, D4FD, D4EA, D4HB, D6EA, G6EN, D3EA |
| Land Rover | ED4 | 204DTD |
| TD4 | 224DT, DW12BTED4, 204D3, M47 | |
| TDV8 | 448DT, 368DT | |
| TD6 | 276DT | |
| TDV6 | 306DT | |
| SDV6 | 30DDTX | |
| SDV8 | 448DT | |
| SD4 | 224DT | |
| Citroën, Peugeot, DS, Volvo | HDI, HDi | DV4TD, DV4TED4, DV6TED4, DV6ATED4, DV6ETED, DW10TD |
| BlueHDi, e-HDi | RHE (DW10CTED4), BHY (DV6FD), BHX (DV6FC), DV6FCTED, DW10FCTED4, DW10FC, DW10FDTED4, DV6FETED, DV6FE, DV5TED4 | |
| Fiat, Alfa Romeo, Lancia | JTD | 182 B4.000, 188 A2.000, 185 A6.000, 839 A5.000, 186 A6.000, 182 B4.000, 182 B9 .000, AR 34202, AR 32501, 937 A2.000 |
| JTDm | 955 A4.000, 955 A3.000, 198 A2.000, 939 A7.000, 937 A6.000 | |
| MultiJet | 188 A8.000, 188 A9.000, 198 A3.000, 199 B1.000 , 263 A1,000 | |
| Audi, Škoda, Volkswagen, Seat | TDI | CVMD, CAAC, DCXA, DBGC, DFGA, CLJA, CBAB ,CAYC, BKS, BMK, CASA, CJMA, CRCA, CDUD, CKDA, DCZA |
| BiTDi | CDCA, CNEA, CSHA | |
| Isuzu | DDi iTEQ | 4JJ1 |
| Chevrolet, Daewoo | VCDi | Z20S, Z20DMH, LLW, Z20S1, Z20D1, Z22D1 |
| Honda | i-DTEC | N16A, N16A2, N22B1, N16A3, N22B3, N22B4 |
| i-CTDi | N22A1, N22A3 | |
| CTDI | N22A2 | |
| Mazda | MZR-CD | RF7J, R2AA, RF5C, RF7J, Y601, Y642 |
| Skyactiv-D | S5-DPTS, S8-DPTS, SH-VPTS | |
| D | SHY1 | |
| CiTD | RF5C | |
| DI Turbo | Y601 | |
| Mitsubishi | DI-D | 4N13, 4N14, 4N15 |
| SsangYong | XDi | D20DT, D27DT |
| eXDI | D20DTF | |
| XVT | D27DTP | |
| Volvo | Drive-E | D4204T8, D4204T14, D4204T23, D 4162 T |
| D2 | D5204T7, D4162T | |
| D3 | D5204T5 | |
| D4 | D4204T5, D5204T | |
| D5 | D5244T, D5244T5, D5244T15, D 5244 T9 | |
| Chrysler, Jeep | CRD | ENC, ENJ, ENS, ENR, EXF, EXA, ENE, ENF, EXL |
| BMW, MINI | d | N47 D20 C, N57 D30 A, N57 D30 B, B37 C15 A |
| SD, D | N47C20A | |
| Ford | TDCi | F6JB, HHJC, UGJC, XVJA, XVJC, T1WB, QYBA, KHBA, T8CC, T1GA |
| Duratorq-TDCi | DV4TD, F6JA , F6JB, DV4TED4 | |
| Saab | TiD | Z19DT, Z19DTH, D223L |
| TTiD | A19DTR, Z19DTR, A 20 DTR | |
| Toyota | D-4D | 1ND-TV, 1WW, 1AD-FTV, 2KD-FTV |
| D-CAT | 2AD-FHV | |
| Porsche | Diesel | M05.9E, M05.9D, MCU.DB, MCN.RB, MCR.CA, MCR.C, MCU.DC |
| Infinity | d | V9X, OM651 |
| Subaru | D | EE20Z |
Main components of the common rail system
| Number | Name | Function |
| 1 | Low pressure fuel pump | This is located in the fuel tank and supplies fuel to the high pressure pump. |
| 2 | Fuel filter | This removes dirt and various impurities from the fuel and prevents wear on the pump and injectors. |
| 3 | High-pressure pump | This leads the fuel under pressure to the distributor pipe. |
| 4 | Fuel metering valve | This precisely adjusts the amount of fuel supplied to the high-pressure fuel pump . |
| 5 | Fuel pressure sensor | This measures the pressure in the fuel rail and then sends a corresponding signal to the control unit. |
| 6 | Fuel tube | This contains fuel under high pressure. |
| 7 | Pressure Limiter | This relieves pressure on the fuel rail and returns excess fuel to the fuel tank. It is also controlled by the control unit. |
| 8 | Injectors | These throttle the fuel and spray it into the combustion chambers. |
Advantages and disadvantages of common-rail engines
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| 🟢 Fuel efficiency | 🔴 Very sensitive to fuel quality |
| 🟢 Environmentally friendly | 🔴 Sensitivity of injectors to contamination |
| 🟢 Quiet operation | 🔴 It is complicated and expensive to repair |
| 🟢 High torque | 🔴 More frequent replacement of fuel filters |
| 🟢 High performance |
